What is a Filling Machine, and How Does It Work?
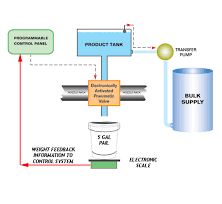
Filling machines play a crucial role in various industries by automating the process of packaging products into containers, whether it’s liquids, powders, or granules. These machines ensure efficiency, accuracy, and consistency in the production line. In this article, we’ll dive into the world of filling machines, exploring their types, functions, and how they operate.
Introduction
Disinfectant Filling machines, also known as fillers, are mechanical devices designed to efficiently and precisely fill various products into containers, such as bottles, cans, and pouches. These machines have revolutionized manufacturing processes across industries by streamlining the packaging process and ensuring product consistency.
For accurate flow rate measurements, having your flow meter properly calibrated per the manufacturer’s recommendations via professional flow meter calibration services ensures reliable data and optimal performance.
Types of Filling Machines
Gravity Fillers
Gravity fillers operate by allowing the product to flow into the container through a nozzle due to gravity. These fillers are suitable for free-flowing liquids and are commonly used in the beverage industry.
Piston Fillers
Piston fillers use a piston to measure and dispense a specific volume of product into containers. They are ideal for filling viscous liquids and products with particulates.
Volumetric Fillers
Volumetric fillers measure a fixed volume of product for each fill cycle. They are versatile and can handle liquids, powders, and granular products.
Auger Fillers
Auger fillers are designed for powdery and granular products. They use an auger screw to dispense a precise amount of product into containers.
Overflow Fillers
Overflow fillers are commonly used for filling liquids into containers with a consistent level. Excess product overflows to maintain a uniform fill level.
Time-Pressure Fillers
Time-pressure fillers operate by using a combination of time and pressure to control the fill level. They are suitable for various liquids and products.
Aseptic Fillers
Aseptic fillers maintain the sterility of both the product and the container. They are crucial in industries such as pharmaceuticals and food, where hygiene is paramount.
Working Principles of Filling Machines
Filling machines follow a series of steps to ensure accurate and efficient filling:
Container Handling
Containers are placed on the conveyor system, which transports them to the filling station.
Product Feeding
The product is fed into the filler’s reservoir or hopper, ready for the filling process.
Filling Process
During filling, the product is dispensed into the containers using the chosen mechanism based on the type of filler.
Level Control
The filling machine ensures that the product reaches a predetermined level in the container, whether through weight, volume, or visual sensors.
Benefits of Filling Machines
Filling machines offer several advantages for manufacturers:
Increased Efficiency
Filling machines automate the packaging process, significantly increasing production rates and reducing labor costs.
Accurate Dosage
Precision is paramount in product packaging. Filling machines ensure consistent and accurate dosages for each container.
Reduced Product Waste
Manual filling can lead to product spillage and waste. Filling machines minimize such losses, contributing to cost savings.
Versatility
Different filling machine types cater to a wide range of products, making them suitable for various industries.
Industries Using Filling Machines
Filling machines find applications in multiple sectors:
Food and Beverage
From beverages to condiments, filling machines are indispensable in the food and beverage industry.
Pharmaceutical
Pharmaceutical companies rely on aseptic fillers to maintain product integrity and safety.
Cosmetics and Personal Care
Creams, lotions, and other personal care products are efficiently filled using these machines.
Chemical and Cleaning
Filling machines handle various chemical products, ensuring accurate and safe packaging.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Proper maintenance ensures optimal performance:
Regular Cleaning
Regular cleaning prevents product residue buildup and maintains hygiene.
Wear and Tear
Replacing worn-out parts promptly prevents downtime and maintains efficiency.
Calibration
Regular calibration is essential to ensure accurate dosing and fill levels.
Common Issues and Solutions
Addressing issues like leaks, misalignment, or sensor errors promptly keeps the production line running smoothly.
Future Trends in Filling Machines
The future holds exciting possibilities:
Automation and Robotics
Advanced automation and robotics will further enhance filling machine efficiency.
IoT Integration
Internet of Things (IoT) technology will enable real-time monitoring and control of filling machines.
Sustainability
Eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs will drive the development of more sustainable filling machines.
Conclusion
Disinfectant Filling machineshave revolutionized the packaging process across industries, ensuring accurate, efficient, and consistent product filling. As technology continues to advance, these machines will play an even more significant role in shaping the future of manufacturing.
FAQs
- What products can be filled using filling machines? Filling machines can handle a wide range of products, including liquids, powders, granules, and even semi-solid substances.
- Are filling machines suitable for small-scale businesses? Yes, modern filling machines come in various sizes, making them adaptable for both small-scale and large-scale businesses.
- How important is calibration for filling machine accuracy? Calibration is crucial for maintaining accurate dosages and fill levels, ensuring product quality and consistency.
- Can filling machines accommodate different container sizes? Yes, many filling machines are adjustable and can accommodate various container sizes and shapes.
- Are there eco-friendly options for filling machines? Absolutely, the industry is moving towards more sustainable options, with the development of eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs.




