What is the Difference Between Enzyme Assay and ELISA?
Enzymes are fascinating biological molecules that play a crucial role in various biochemical processes. Scientists utilize different techniques to study and quantify enzyme activity. Two commonly used methods are enzyme assay and ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay). While both techniques involve enzymes and contribute to scientific research, they serve distinct purposes and have unique methodologies.
1. Introduction
Enzyme assays and Elisa Washer are fundamental tools in biochemistry and molecular biology. They provide insights into enzyme activity, protein interactions, and disease detection. Understanding the differences between these techniques is crucial for researchers and clinicians alike.
2. Enzyme Assay: Understanding the Basics
Principles of Enzyme Assays
Enzyme assays involve measuring the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. They provide quantitative data about enzyme activity under specific conditions. Enzyme assays typically require a substrate (the molecule that the enzyme acts upon) and involve monitoring the appearance of a product or the disappearance of a substrate.
Types of Enzyme Assays
There are various types of enzyme assays, including spectrophotometric assays, radioactive assays, and fluorometric assays. Spectrophotometric assays, for instance, rely on measuring changes in absorbance to determine enzyme activity. These assays are versatile and widely used in research and diagnostics.
3. ELISA: A Brief Overview
Principles of ELISA
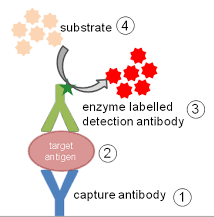
ELISA is a powerful technique used to detect and quantify specific molecules, such as proteins, peptides, hormones, and antibodies, in biological samples. It involves the use of antibodies that bind to the target molecule, allowing for its detection.
Different Types of ELISA
There are different variations of ELISA, including direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive ELISA. Each variant has its unique applications and advantages. For example, sandwich ELISA is often used to detect antigens in complex biological samples.
4. Key Differences Between Enzyme Assay and ELISA
Purpose and Application
Enzyme assays focus on measuring enzyme activity and are used to study various enzymatic reactions. ELISA, on the other hand, is employed to detect and quantify specific molecules, making it a valuable tool in medical diagnostics and research.
Methodology and Procedure
Enzyme assays involve monitoring changes in substrate or product concentration. ELISA, however, relies on the binding between antibodies and antigens, utilizing colorimetric or fluorescent signals for detection.
Sensitivity and Specificity
ELISA is known for its high sensitivity and specificity, making it an excellent choice for detecting low concentrations of target molecules. Enzyme assays can also be sensitive but might require more optimization to achieve comparable results.
Detection and Quantification
Enzyme assays measure changes in optical properties, while ELISA detects the binding of antibodies and antigens. ELISA provides quantitative data, whereas enzyme assays often require additional steps for accurate quantification.
Time and Complexity
Enzyme assays are relatively quicker to perform compared to ELISA, which involves multiple incubation and washing steps. ELISA can be more complex and time-consuming but offers higher sensitivity.
5. Choosing the Right Method for Your Study
Selecting the appropriate technique depends on the research objectives. Enzyme assays are suitable for understanding enzyme kinetics, while ELISA is essential for detecting specific molecules, such as pathogens or biomarkers.
6. Conclusion
In the realm of biochemical research and medical diagnostics, both enzyme assays and Elisa Washer play pivotal roles. While enzyme assays provide insights into general enzyme activity, ELISA offers a targeted approach for detecting and quantifying specific molecules. Understanding their differences enables researchers to make informed decisions and achieve accurate results.
7. FAQs
1. What is the main objective of an enzyme assay?
An enzyme assay aims to measure enzyme activity and understand how enzymes function under specific conditions.
2. How does ELISA contribute to medical diagnostics?
ELISA is used in medical diagnostics to detect biomarkers, antibodies, and pathogens, aiding in the early detection of diseases.
3. Can enzyme assays and ELISA be used interchangeably?
Enzyme assays and ELISA serve different purposes and are not interchangeable. Enzyme assays measure enzyme activity, while ELISA detects specific molecules.
4. Are there any disadvantages to using ELISA?
ELISA can be time-consuming and involve multiple steps. Additionally, false positives or negatives can occur if not properly optimized.
5. Where can I learn more about enzyme assays and ELISA techniques?
You can find detailed information in biochemical textbooks, scientific journals, and online research articles.